
Accounts payable, accrued liabilities, and taxes payable are usually classified as current liabilities. If a portion of a long-term debt is payable within the next year, that portion is classified https://www.bookstime.com/ as a current liability. Knowing what goes into preparing these documents can also be insightful. Assets and liabilities are two fundamental components of a company’s financial statements.
Based on their durations, liabilities are broadly classified into short-term and long-term liabilities. Short-term liabilities, also known as current liabilities, are obligations that are typically due within a year. On the other hand, long-term liabilities, or non-current liabilities, extend beyond a year. Besides these two primary categories, contingent liabilities and other specific cases may also exist, further adding complexity to accounting practices.
Assets, liabilities, and equity
The liabilities definition in financial accounting is a business’s financial responsibilities. A common liability for small businesses is accounts payable, or money owed to suppliers. Liabilities and equity make up the right side of the balance sheet and cover the financial side of the company. With liabilities, this is obvious—you owe loans to a bank, or repayment of bonds to holders of debt. Liabilities are listed at the top of the balance sheet because, in case of bankruptcy, they are paid back first before any other funds are given out. Non-current liabilities can also be referred to as long-term liabilities.
- A certified public accountant (CPA) is a type of professional accountant with more training and experience than a typical accountant.
- Then, current and fixed assets are subtotaled and finally totaled together.
- Some companies will class out their PP&E by the different types of assets, such as Land, Building, and various types of Equipment.
- Referring again to the AT&T example, there are more items than your garden variety company that may list one or two items.
- For example, a positive change in plant, property, and equipment is equal to capital expenditure minus depreciation expense.
- In business, assets are the things that are considered of value for the business.
Liabilities play a crucial role in evaluating a company’s financial health. By analyzing the types, amounts, and trends of a company’s liabilities, it is possible to gauge its financial position, stability, and risk exposure. A company with too many liabilities compared to its assets may face cash flow problems or increased financial risk.
How are assets and liabilities related and treated differently in financial statements?
These expenses include items such as wages, rent, utilities, and other expenditures necessary to keep the business running smoothly. In accounting, operating expenses are recorded as liabilities until they are paid off. For example, wages payable are considered a liability as it represents the amount owed to employees for their work but not yet paid. When presenting liabilities on the balance sheet, they must be classified as either current liabilities or long-term liabilities. A liability is classified as a current liability if it is expected to be settled within one year.
In very specific contract liabilities, failure to pay on the installment date will produce penalties, and such penalties can also be considered a cost of having liabilities. Balance sheet presentations differ, but the concept remains the same. Some businesses prefer the account-form balance sheet, wherein assets are presented on the left side while liabilities and equity are presented on the right (see highlighted part). Accounts Payables, or AP, is the amount a company owes suppliers for items or services purchased on credit. As the company pays off its AP, it decreases along with an equal amount decrease to the cash account. The most liquid of all assets, cash, appears on the first line of the balance sheet.
Liabilities vs. Expenses
Liabilities can take various forms, like loans, mortgages, or accounts payable, and play a significant role in determining a company’s financial health and risk. They are vital components of a balance sheet, which is one of the primary financial statements used by stakeholders to assess a company’s performance and sustainability. In accounting, liabilities are debts your liabilities in accounting business owes to other people and businesses. Examples of liabilities include bank loans, IOUs, promissory notes, salaries of employees, and taxes. Liabilities are on the right side of the balance sheet, and these accounts have a normal credit balance. It means that crediting liability accounts increases their balances while debiting them decreases their balances.
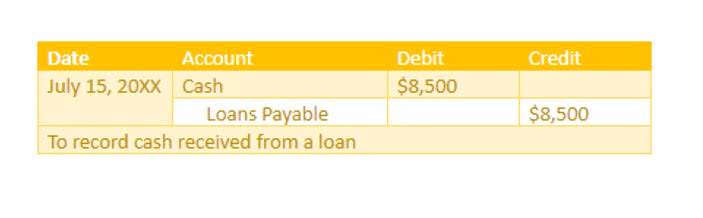
For example, if a company takes on a bank loan to be paid off in 5-years, this account will include the portion of that loan due in the next year. Inventory includes amounts for raw materials, work-in-progress goods, and finished goods. The company uses this account when it reports sales of goods, generally under cost of goods sold in the income statement. These obligations can offer insights into a company’s ability to manage its debts and its potential capacity to take on additional financing in the future. In conclusion, proper recognition and measurement of liabilities are essential for maintaining accurate and transparent financial statements. Understanding the criteria and measurement methods for liabilities helps organizations maintain a clear and confident financial position while facilitating informed decision-making.